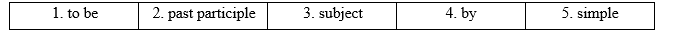Tiếng Anh 12 Unit 6 6B. Grammar1 SPEAKING Work in pairs. In what ways do you think these things were different in the past? 2 Read the text. Does it mention your ideas from exercise 1? 3 Find passive examples of tenses (a-g) in the text. 4 Read the Learn this! box. Complete the rules.
Lựa chọn câu để xem lời giải nhanh hơn
Bài 1 1 SPEAKING Work in pairs. In what ways do you think these things were different in the past? (Làm việc theo cặp. Bạn nghĩ những điều này khác biệt như thế nào trong quá khứ?) diseases hospitals hygiene Lời giải chi tiết: *Diseases: In the past, knowledge about diseases was limited and treatment methods often relied on superstition or folk remedies rather than evidence-based medicine. Communicable diseases such as smallpox, typhoid fever, and cholera often caused high mortality rates, especially among children. Life expectancy was lower due to the widespread transmission of infectious diseases. (*Bệnh tật: Trước đây, kiến thức về bệnh tật còn hạn chế và phương pháp điều trị thường dựa vào mê tín hoặc các bài thuốc dân gian hơn là dùng thuốc dựa trên bằng chứng. Các bệnh truyền nhiễm như đậu mùa, sốt thương hàn, dịch tả thường gây ra tỷ lệ tử vong cao, đặc biệt là ở trẻ em. Tuổi thọ thấp hơn do sự lây lan rộng rãi của các bệnh truyền nhiễm.) *Hospitals: Historical hospitals were typically basic facilities with poor sanitation, serving as places of last resort for the poor and sick. Medical procedures were performed with limited understanding of anesthesia, sterilization, and hygiene practices, resulting in high infection and mortality rates. (* Bệnh viện: Bệnh viện lịch sử thường là cơ sở vật chất cơ bản với điều kiện vệ sinh kém, là nơi nghỉ dưỡng cuối cùng của người nghèo và người bệnh. Các thủ tục y tế được thực hiện với sự hiểu biết hạn chế về thực hành gây mê, khử trùng và vệ sinh, dẫn đến tỷ lệ nhiễm trùng và tử vong cao.) *Hygiene: In the past, hygiene practices were simpler compared to modern standards. Clean water, sewage systems, and waste management were often inadequate, leading to the spread of waterborne diseases and unsanitary living conditions. Personal hygiene habits were lacking due to limited access to clean water, soap, and hygiene products. (*Vệ sinh: Trước đây, việc thực hành vệ sinh đơn giản hơn so với tiêu chuẩn hiện đại. Nước sạch, hệ thống thoát nước và quản lý chất thải thường không đầy đủ, dẫn đến sự lây lan của các bệnh lây truyền qua đường nước và điều kiện sống mất vệ sinh. Thói quen vệ sinh cá nhân còn thiếu do khả năng tiếp cận nước sạch, xà phòng và các sản phẩm vệ sinh bị hạn chế.) Bài 2 2 Read the text. Does it mention your ideas from exercise 1? (Đọc văn bản. Nó có đề cập đến ý tưởng của bạn từ bài tập 1 không?) A history of hygiene Ancient ideas of hygiene The ancient Greeks and Egyptians enjoyed relatively high standards of personal hygiene - they had been taught about the importance of cleanliness by their religious leaders. But it was the Romans who developed the first public toilets and enormous public baths. 19th century developments Louis Pasteur and Joseph Lister's revolutionary ideas about using sterile instruments in clean hospitals were adopted in the 19th century. Before then, up to half of Lister's patients who had survived surgery were being killed by infections spread by germs. Infection and disease haven't been eliminated entirely in our hospitals yet, but they have been significantly reduced. Today and tomorrow Although hygiene in developing countries is being improved all the time, 36% of the world's population is still affected by poor hygiene. Furthermore, medical organisations will be challenged in the future by new infections and diseases; the world's population is so closely connected that potentially catastrophic epidemics will be transmitted around the globe in days. Phương pháp giải: Tạm dịch Lịch sử vệ sinh Ý tưởng cổ xưa về vệ sinh Người Hy Lạp và Ai Cập cổ đại có tiêu chuẩn vệ sinh cá nhân tương đối cao - họ đã được các nhà lãnh đạo tôn giáo của họ dạy về tầm quan trọng của sự sạch sẽ. Nhưng chính người La Mã mới là người đã phát triển những nhà vệ sinh công cộng đầu tiên và những nhà tắm công cộng khổng lồ. Sự phát triển của thế kỷ 19 Ý tưởng mang tính cách mạng của Louis Pasteur và Joseph Lister về việc sử dụng dụng cụ vô trùng trong bệnh viện sạch đã được áp dụng vào thế kỷ 19. Trước đó, có tới một nửa số bệnh nhân sống sót sau cuộc phẫu thuật của Lister đã tử vong do nhiễm trùng do vi trùng lây lan. Nhiễm trùng và bệnh tật vẫn chưa được loại bỏ hoàn toàn trong các bệnh viện của chúng ta, nhưng chúng đã giảm đi đáng kể. Hôm nay và ngày mai Mặc dù vấn đề vệ sinh ở các nước đang phát triển ngày càng được cải thiện nhưng 36% dân số thế giới vẫn bị ảnh hưởng bởi tình trạng vệ sinh kém. Hơn nữa, các tổ chức y tế sẽ gặp thách thức trong tương lai bởi các bệnh nhiễm trùng và bệnh tật mới; dân số thế giới được kết nối chặt chẽ đến mức những dịch bệnh thảm khốc có thể xảy ra sẽ lan tràn khắp toàn cầu trong vài ngày tới. Bài 3 3 Find passive examples of tenses (a-g) in the text. (Tìm ví dụ bị động về các thì (a-g) trong văn bản.) a present simple b present perfect c past continuous d will future e present continuous f past simple g past perfect Lời giải chi tiết: a present simple (thì hiện tại đơn) Thông tin: “36% of the world's population is still affected by poor hygiene.” (36% dân số thế giới vẫn bị ảnh hưởng bởi tình trạng vệ sinh kém.) b present perfect (hiện tại hoàn thành) Thông tin: “Infection and disease haven't been eliminated entirely in our hospitals yet, but they have been significantly reduced.” (Sự lây nhiễm và bệnh tật vẫn chưa được loại bỏ hoàn toàn ở các bệnh viện của chúng ta, nhưng chúng đã giảm đi đáng kể.) c past continuous (quá khứ tiếp diễn) Thông tin: “up to half of Lister's patients who had survived surgery were being killed by infections spread by germs.” (có tới một nửa số bệnh nhân sống sót sau cuộc phẫu thuật của Lister đã tử vong do nhiễm trùng do vi trùng lây lan.) d will future (thì tương lai will) Thông tin: “medical organisations will be challenged in the future by new infections and diseases;” (các tổ chức y tế sẽ bị thách thức trong tương lai bởi các bệnh nhiễm trùng và bệnh tật mới;) e present continuous (hiện tại tiếp diễn) Thông tin: “Although hygiene in developing countries is being improved all the time,” (Mặc dù vệ sinh ở các nước đang phát triển luôn được cải thiện,) f past simple (quá khứ đơn) Thông tin: “Louis Pasteur and Joseph Lister's revolutionary ideas about using sterile instruments in clean hospitals were adopted in the 19th century.” (Ý tưởng mang tính cách mạng của Louis Pasteur và Joseph Lister về việc sử dụng dụng cụ vô trùng trong bệnh viện sạch đã được áp dụng vào thế kỷ 19.) g past perfect (quá khứ hoàn thành) Thông tin: “they had been taught about the importance of cleanliness by their religious leaders.” (họ đã được các nhà lãnh đạo tôn giáo của họ dạy về tầm quan trọng của sự sạch sẽ.) Bài 4 4 Read the Learn this! box. Complete the rules. (Đọc phần Learn this! Hoàn thành các quy tắc.) LEARN THIS! The passive 1 We form the passive with the verb 1 ____ and the 2 ____ of the main verb. The object of an active verb can become the 3 ____ of a passive verb. They haven't found a cure for colds yet. (a cure = object) → A cure for colds hasn't been found yet. (a cure = subject) 2 If we need to mention the agent, we use 4 ____ Enormous public baths were built by the Romans. 3 We use the passive: a when we do not know (or do not want or need to say) who does something. b for more formal language, e.g. for processes. First, the coffee beans are dried. Then they are roasted c when we want to focus on the person to whom the action is done, not the person doing the action. 4 We use the 5 ____ and past continuous forms of the passive, but we do not use other continuous forms. Hygiene is being improved.✔ → → They have been improving hygiene.✓ Lời giải chi tiết:
LEARN THIS! LEARN THIS! The passive 1 We form the passive with the verb 1 to be and the 2 past participle of the main verb. The object of an active verb can become the 3 subject of a passive verb. They haven't found a cure for colds yet. (a cure = object) → A cure for colds hasn't been found yet. (a cure = subject) 2 If we need to mention the agent, we use 4 by Enormous public baths were built by the Romans. 3 We use the passive: a when we do not know (or do not want or need to say) who does something. b for more formal language, e.g. for processes. First, the coffee beans are dried. Then they are roasted c when we want to focus on the person to whom the action is done, not the person doing the action. 4 We use the 5 simple and past continuous forms of the passive, but we do not use other continuous forms. Hygiene is being improved.✔ → → They have been improving hygiene.✓ Tạm dịch LEARN THIS! Bị động 1 Chúng ta tạo thành thể bị động với động từ to be và phân từ quá khứ của động từ chính. Tân ngữ của động từ chủ động có thể trở thành chủ ngữ của động từ bị động. Họ vẫn chưa tìm ra cách chữa cảm lạnh. (một phương pháp chữa trị = tân ngữ) → Thuốc chữa cảm lạnh vẫn chưa được tìm ra. (một cách chữa trị = chủ ngữ) 2 Nếu cần đề cập đến tác nhân, chúng ta dùng by Những nhà tắm công cộng khổng lồ được xây dựng bởi người La Mã. 3 Chúng ta sử dụng thể bị động: a khi chúng ta không biết (hoặc không muốn hoặc không cần nói) ai làm việc gì đó. b cho ngôn ngữ trang trọng hơn, ví dụ: cho các quá trình. Đầu tiên, hạt cà phê được sấy khô. Sau đó chúng được nướng c khi chúng ta muốn tập trung vào người thực hiện hành động chứ không phải người thực hiện hành động đó. 4 Chúng ta sử dụng dạng đơn và quá khứ tiếp diễn của thể bị động, nhưng chúng ta không sử dụng các dạng tiếp diễn khác. Vệ sinh ngày càng được cải thiện. ✔ → Vệ sinh đã được cải thiện. X → Họ đã cải thiện vấn đề vệ sinh. ✓ Bài 5 5 Rewrite the sentences (1-5) in the passive. Match them with rules (2-4) in the Learn this! box. The sentences may match with more than one rule. (Viết lại câu (1-5) ở thể bị động. Hãy ghép chúng với các quy tắc (2-4) trong phần Learn this! Các câu có thể phù hợp với nhiều hơn một quy tắc.) 1 A doctor has examined me and told me to rest at home. 2 It was in the 19th century that they invented anaesthetics. 3 Scientists are making more advances in medicine every year. 4 They'll stitch the wound now and remove the stitches next week. 5 Kazimierz Funk, a Polish scientist, discovered the fact that vitamins could cure many diseases. Phương pháp giải: Cách viết câu cấu trúc từ chủ động sang bị động: *Chủ động: S + V + O * Bị động: O + tobe V3/ed (tương ứng với thì) + by S. Lời giải chi tiết: 1 A doctor has examined me and told me to rest at home. (Một bác sĩ đã khám cho tôi và bảo tôi nên nghỉ ngơi ở nhà.) => I have been examined by a doctor and been told to rest at home. => Rule 2 (Tôi đã được bác sĩ khám và bảo nghỉ ngơi ở nhà.) 2 It was in the 19th century that they invented anaesthetics. (Vào thế kỷ 19, người ta đã phát minh ra thuốc gây mê.) => Anaesthetics were invented in the 19th century. => Rule 3a (Thuốc gây mê được phát minh vào thế kỷ 19.) 3 Scientists are making more advances in medicine every year. (Các nhà khoa học đang đạt được nhiều tiến bộ hơn trong y học mỗi năm.) => More advances in medicine are being made by scientists every year. => Rule 2 and 3b (Nhiều tiến bộ hơn trong y học đang được các nhà khoa học thực hiện hàng năm.) 4 They'll stitch the wound now and remove the stitches next week. (Họ sẽ khâu vết thương ngay bây giờ và tháo chỉ vào tuần tới.) => The wound will be stitched now and the stitches will be removed next week. => Rule 3b (Vết thương sẽ được khâu ngay bây giờ và vết khâu sẽ được tháo ra vào tuần sau.) 5 Kazimierz Funk, a Polish scientist, discovered the fact that vitamins could cure many diseases. (Kazimierz Funk, một nhà khoa học người Ba Lan, đã phát hiện ra sự thật rằng vitamin có thể chữa được nhiều bệnh.) => The fact that vitamins could cure many diseases was discovered by Kazimierz Funk, a Polish scientist. => Rule 2 and 3b (Việc vitamin có thể chữa được nhiều bệnh đã được Kazimierz Funk, một nhà khoa học người Ba Lan phát hiện.) Bài 6 6 Read the text below. Then rewrite the underlined sentences (1-8) in the passive. Decide whether you need to include the agent. (Đọc văn bản dưới đây. Sau đó viết lại các câu được gạch chân (1-8) ở thể bị động. Quyết định xem bạn có cần thêm tác nhân hay không.) It was called 'The Great Mortality, but today 1 we know it as the Black Death. In 1348, 2 rats brought the plague from Asia - to Europe. 3 The disease killed millions of people. The cities were overcrowded with frightened people and 4 coughs and sneezes quickly infected them. Similarly, in 2019, 5 COVID-19 attacked different areas of the world. 6 The virus corona infected millions of people. 7 Authorities had to lock down many cities to stop the infection. This virus is still popular but 8 vaccines can save patients from danger. Phương pháp giải: Cách viết câu cấu trúc từ chủ động sang bị động: *Chủ động: S + V + O * Bị động: O + tobe V3/ed (tương ứng với thì) + by S. - Không cần dùng “by” khi tác nhân là I, you, we, they, he, she, it, people, everyone, someone… Lời giải chi tiết: 1 we know it as the Black Death. (chúng ta gọi nó là Cái chết đen.) => It is known as the Black Death. (Nó được gọi là Cái chết đen.) 2 rats brought the plague from Asia - to Europe. (con chuột đã mang bệnh dịch hạch từ châu Á tới châu Âu.) => The plague was brought from Asia to Europe by rats. (Bệnh dịch hạch được chuột mang từ châu Á sang châu Âu.) 3 The disease killed millions of people. (Căn bệnh này đã giết chết hàng triệu người.) => Millions of people were killed by the disease. (Hàng triệu người đã thiệt mạng vì căn bệnh này.) 4 coughs and sneezes quickly infected them. (cái ho và hắt hơi nhanh chóng nhiễm cho họ.) => They were quickly infected by coughs and sneezes. (Họ nhanh chóng bị lây nhiễm qua ho và hắt hơi.) 5 COVID-19 attacked different areas of the world. (Covid-19 tấn công nhiều khu vực khác nhau trên thế giới.) => Different areas of the world were attacked by COVID-19. (Các khu vực khác nhau trên thế giới đã bị COVID-19 tấn công.) 6 The virus corona infected millions of people. (Virus corona lây nhiễm hàng triệu người.) => Millions of people were infected by the corona virus. (Hàng triệu người đã bị nhiễm virus corona.) 7 Authorities had to lock down many cities (Nhà chức trách phải phong tỏa nhiều thành phố) => Many cities had to be locked down by authorities. (Nhiều thành phố đã bị chính quyền phong tỏa.) 8 vaccines can save patients from danger. (vắc xin có thể cứu bệnh nhân khỏi nguy hiểm) => Patients can be saved from danger by vaccines. (Bệnh nhân có thể được cứu khỏi nguy hiểm nhờ vắc xin.) Bài 7 7 SPEAKING Work in pairs. Talk about these things. (Làm việc theo cặp. Nói về những điều này.) 1 The funniest joke you've been told (Câu chuyện cười hài hước nhất mà bạn từng được kể) 2 A job you'd like to be offered (Một công việc bạn muốn được mời) Phương pháp giải: Bài tham khảo A: Hey, do you remember the funniest joke you've ever been told? B: Oh yeah, it was this one about a talking dog. So, there's this guy walking down the street with his dog, right? And they come across this sign that says, "Talking Dog for Sale." The guy's curious, so he goes up to the owner and asks, "Does your dog really talk?" And the owner says, "Yep, sure does. Go ahead, ask him a question." So, the guy bends down to the dog and asks, "Hey, buddy, what's on top of a house?" And the dog goes, "Roof!" I couldn't stop laughing! A: Haha, that's hilarious! I can see why you found it funny. B: Have you thought about the job you'd like to be offered? A: I've been dreaming about working as a travel photographer. Imagine getting paid to explore the world and capture its beauty through my lens. It would be a dream come true! I'd get to visit all these exotic locations and capture breathtaking moments. Plus, my photos would inspire so many people to travel and explore. B: I couldn't agree more. I hope you get the opportunity to pursue your dream job soon! Tạm dịch A: Này, bạn có nhớ câu chuyện cười hài hước nhất mà bạn từng được kể không? B: Ồ vâng, đó là câu chuyện về một con chó biết nói. Có anh chàng này đang đi dạo trên phố với con chó của mình phải không? Và họ bắt gặp tấm biển có dòng chữ "Bán chó biết nói". Anh chàng tò mò nên đến gần người chủ và hỏi: "Con chó của bạn có biết nói thật không?" Và người chủ nói: "Ừ, chắc chắn rồi. Cứ hỏi nó một câu đi." Vì vậy, anh chàng cúi xuống con chó và hỏi, "Này anh bạn, trên nóc nhà có gì thế?" Và con chó nói: "Mái nhà!" Tôi không thể ngừng cười! A: Haha, buồn cười quá! Tôi có thể hiểu tại sao bạn thấy nó buồn cười. B: Bạn đã nghĩ về công việc bạn muốn được mời chưa? A: Tôi đã mơ ước được làm nhiếp ảnh gia du lịch. Hãy tưởng tượng bạn được trả tiền để khám phá thế giới và ghi lại vẻ đẹp của nó qua ống kính của mình. Giấc mơ sẽ trở thành hiện thực! Tôi sẽ được đến thăm tất cả những địa điểm kỳ lạ này và ghi lại những khoảnh khắc ngoạn mục. Thêm vào đó, những bức ảnh của tôi sẽ truyền cảm hứng cho rất nhiều người đi du lịch và khám phá. B: Tôi không thể đồng ý hơn được. Chúc bạn sớm có cơ hội theo đuổi công việc mơ ước của mình!
|