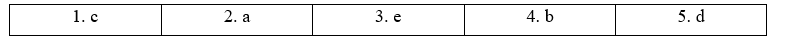Tiếng Anh 11 Grammar Builder – Unit 81 Write third conditional sentences. Use the verbs in brackets. 2 Rewrite the two sentences as one. Use the third conditional. 1 Rewrite the sentences using participle clauses to replace the relative clauses. 1 Match the reply questions (a-e) with the statements (1-5). 2 Write reply questions for these statements. Tổng hợp đề thi học kì 2 lớp 11 tất cả các môn - Chân trời sáng tạo Toán - Văn - Anh - Lí - Hóa - Sinh
Lựa chọn câu để xem lời giải nhanh hơn
8.1 The third conditional Bài 1 8.1 The third conditional (Câu điều kiện loại ba) We form the third conditional with if + past perfect, would have + past participle. If you'd gone to bed earlier, you wouldn't have fallen asleep in class. We use the third conditional to talk about imaginary situations and to say how things could have been different in the past. If we'd left earlier, we wouldn't have missed the train. We often use if to express regret or criticism. If you'd been more careful, you wouldn't have dropped those plates. You would have passed your exams if you'd worked a bit harder. We can also put the if clause at the end of the sentence. I'd have invited you if I'd known you liked fancy-dress parties. Notice the short forms used in third conditional sentences. The short form of both had and would is 'd. If I'd had more money, I'd have paid for you. In spoken English, we often shorten both would and have in the main clause. However, in written English, we don't usually shorten both forms. Spoken: If I hadn't run out of petrol, I'd've come by car. Written: If I hadn't run out of petrol, I'd have come by car. Tạm dịch Chúng ta hình thành câu điều kiện loại ba với if + quá khứ hoàn thành, would have + quá khứ phân từ. Nếu bạn đi ngủ sớm hơn, bạn đã không ngủ gục trong lớp. Chúng ta sử dụng câu điều kiện loại ba để nói về những tình huống tưởng tượng và để nói rằng mọi thứ có thể khác đi như thế nào trong quá khứ. Nếu chúng tôi rời đi sớm hơn, chúng tôi đã không bị lỡ chuyến tàu. Chúng ta thường dùng if để bày tỏ sự hối tiếc hoặc chỉ trích. Nếu bạn cẩn thận hơn, bạn đã không làm rơi những chiếc đĩa đó. Bạn sẽ vượt qua kỳ thi của mình nếu bạn làm việc chăm chỉ hơn một chút. Chúng ta cũng có thể đặt mệnh đề if ở cuối câu. Tôi đã mời bạn nếu tôi biết bạn thích những bữa tiệc ăn mặc sang trọng. Lưu ý các dạng rút gọn được sử dụng trong câu điều kiện loại ba. Dạng viết tắt của cả hai had và would là 'd. Nếu tôi có nhiều tiền hơn, tôi đã trả tiền cho bạn rồi. Trong văn nói tiếng Anh, chúng ta thường rút gọn cả would và have trong mệnh đề chính. Tuy nhiên, trong văn viết tiếng Anh, chúng ta thường không rút gọn cả hai dạng này. Nói: Nếu tôi không hết xăng, tôi đã đến bằng ô tô. (I'd've) Viết: Nếu tôi không hết xăng, tôi đã đến bằng ô tô. (I'd have)
1 Write third conditional sentences. Use the verbs in brackets. (Viết câu điều kiện loại ba. Sử dụng động từ trong ngoặc.) 1 If I ______________ (drive) faster, we ______________ (arrive) before six. 2 If Mary ______________ (get) to the cinema earlier, she ______________(see) the start of the film. 3 You ______________ (know) what to do if you ______________ (listen) to the instructions. 4 You ______________ (not cut) yourself if you ______________ (not be) so careless with the knife. 5 If I ______________ (have) the time, I ______________ (call) you. 6 I ______________ (not get) angry if you (not be) so rude! 7 Do you think you ______________(pass) your exams if you ______________ (work) harder? Phương pháp giải: - Cấu trúc câu điều kiện loại ba: If + S + had + V3/ed, S + would / could + have V3/ed *Nghĩa của từ vựng drive – drove – driven (v): lái get – got – got (v): đến see – saw – seen (v): thấy cut – cut – cut (v): cắt be – was / were – been: thì, là, ở know – knew – known (v): biết listen – listened – listened (v): nghe have – had – had (v): có call – called – called (v): gọi pass – passed – passed (v): vượt qua work – worked – worked (v): làm việc Lời giải chi tiết:
1 If I had driven (drive) faster, we would have arrived (arrive) before six. (Nếu tôi đã lái xe nhanh hơn, chúng tôi sẽ đến trước sáu giờ.) 2 If Mary had got (get) to the cinema earlier, she would have seen (see) the start of the film. (Nếu Mary đến rạp chiếu phim sớm hơn thì cô ấy đã xem được đoạn đầu của bộ phim.) 3 You would have known (know) what to do if you had listened (listen) to the instructions. (Bạn sẽ biết phải làm gì nếu bạn đã nghe hướng dẫn.) 4 You would not have cut (not cut) yourself if you had not been (not be) so careless with the knife. (Bạn sẽ không bị đứt tay nếu bạn không quá bất cẩn với con dao.) 5 If I had had (have) the time, I would have called (call) you. (Nếu tôi đã có thời gian, tôi sẽ gọi cho bạn.) 6 I would not have got (not get) angry if you had not been (not be) so rude! (Tôi sẽ không tức giận nếu bạn không thô lỗ như vậy!) 7 Do you think you would have passed (pass) your exams if you had worked (work) harder? (Bạn có nghĩ rằng bạn sẽ vượt qua kỳ thi của bạn nếu bạn đã làm việc chăm chỉ hơn?) 8.1 The third conditional Bài 2 2 Rewrite the two sentences as one. Use the third conditional. (Viết lại hai câu thành một. Sử dụng câu điều kiện loại ba.) 1 You didn't go to bed early. You were tired the following morning. (Bạn đã không đi ngủ sớm. Bạn đã cảm thấy mệt mỏi vào sáng hôm sau.) If you'd gone to bed early, you wouldn't have been tired the following morning. (Nếu bạn đi ngủ sớm, bạn sẽ không mệt mỏi vào sáng hôm sau.) 2 Emma didn't catch the bus. She had to walk to school. 3 The tickets were expensive. I didn't travel by plane. 4 I ate too much. I felt ill. 5 I spent all my money. I was broke. 6 I took a painkiller. My headache went away. 7 We didn't save a lot of money. We weren't able to buy a new car. Phương pháp giải: - Cấu trúc câu điều kiện loại ba: If + S + had + V3/ed, S + would / could + have V3/ed Lời giải chi tiết: 2 Emma didn't catch the bus. She had to walk to school. (Emma không bắt xe buýt. Cô phải đi bộ đến trường.) Đáp án: If Emma had caught the bus, she wouldn't have had to walk to school. (Nếu Emma bắt xe buýt, cô ấy sẽ không phải đi bộ đến trường.) 3 The tickets were expensive. I didn't travel by plane. (Vé đắt. Tôi đã không đi du lịch bằng máy bay.) Đáp án: If the tickets hadn't been expensive, I would have travelled by plane. (Nếu vé không đắt thì tôi đã đi máy bay rồi.) 4 I ate too much. I felt ill. (Tôi đã ăn quá nhiều. Tôi thấy mệt.) Đáp án: If I hadn't eaten too much, I wouldn't have felt ill. (Nếu tôi không ăn quá nhiều, tôi sẽ không thấy mệt.) 5 I spent all my money. I was broke. (Tôi đã tiêu hết tiền của mình. Tôi đã bị cháy túi.) Đáp án: If I hadn't spent all my money, I wouldn't have been broke. (Nếu tôi không tiêu hết tiền thì tôi đã không bị cháy túi.) 6 I took a painkiller. My headache went away. (Tôi đã uống thuốc giảm đau. Cơn đau đầu của tôi biến mất.) Đáp án: If I hadn't taken a painkiller, my headache wouldn't have gone away. (Nếu tôi không uống thuốc giảm đau, cơn đau đầu của tôi sẽ không biến mất.) 7 We didn't save a lot of money. We weren't able to buy a new car. (Chúng tôi đã không tiết kiệm được nhiều tiền. Chúng tôi không thể mua một chiếc ô tô mới.) Đáp án: If we had saved a lot of money, we would have been able to buy a new car. (Nếu chúng tôi tiết kiệm được nhiều tiền, chúng tôi đã có thể mua một chiếc ô tô mới.) 8.2 Participle clauses Bài 1 8.2 Participle clauses (Mệnh đề phân từ) We use participle clauses to give more information about a noun. They can be described as shortened relative clauses (defining or non-defining). Defining: A woman wearing a yellow T-shirt ran out of the shop. (= who was wearing a yellow T-shirt) Non-defining: Her uncle, looking anxious, was standing on the pavement. (= who was looking anxious)
Participle clauses can begin with either a present participle (-ing form) or past participle. Clauses with a present participle (-ing form) replace an active verb. The verb they replace can be in any tense. Outside the café, there was a man selling postcards. (= who was selling postcards) She gave me a box containing some old letters. (= which contained some old letters) Clauses with a past participle replace a passive verb. The verb they replace can be in any tense. A Roman vase found in France last year is being sold. (= which was found in France last year) Tạm dịch Chúng ta sử dụng mệnh đề phân từ để cung cấp thêm thông tin về danh từ. Chúng có thể được mô tả dưới dạng mệnh đề quan hệ rút gọn (xác định hoặc không xác định). Xác định: Một người phụ nữ mặc áo phông màu vàng chạy ra khỏi cửa hàng. (= người đang mặc áo phông màu vàng) Không xác định: Chú của cô, trông có vẻ lo lắng, đang đứng trên vỉa hè. (= người đang trông có vẻ lo lắng)
Mệnh đề phân từ có thể bắt đầu bằng hiện tại phân từ (dạng -ing) hoặc quá khứ phân từ. Các mệnh đề có phân từ hiện tại (dạng -ing) thay thế động từ chủ động. Động từ mà chúng thay thế có thể ở bất kỳ thì nào. Bên ngoài quán cà phê, có một người đàn ông bán bưu thiếp. (= người mà đang bán bưu thiếp) Cô ấy đưa cho tôi một chiếc hộp chứa một số lá thư cũ. (= cái mà chứa một số chữ cái cũ) Mệnh đề với quá khứ phân từ thay thế động từ bị động. Động từ mà chúng thay thế có thể ở bất kỳ thì nào. Một chiếc bình La Mã được tìm thấy ở Pháp năm ngoái đang được bán. (= cái mà được tìm thấy ở Pháp năm ngoái)
1 Rewrite the sentences using participle clauses to replace the relative clauses. (Viết lại câu sử dụng mệnh đề phân từ để thay thế mệnh đề quan hệ.) 1 I saw three men who were arguing about a taxi. (Tôi thấy ba người đàn ông những người mà đang tranh cãi về một chiếc taxi.) I saw three men arguing about a taxi. (Tôi thấy ba người đàn ông tranh cãi về một chiếc taxi.) 2 We talked to a young man who wanted to study in England. 3 A suspected burglar, who had been arrested by the police, has escaped. 4 My uncle bought a pen that was made of gold. 5 She was wearing a necklace that belonged to her grandmother. 6 Three men, who were coming out of the restaurant late at night, saw the robbery. Phương pháp giải: Đại từ quan hệ + V => rút động từ về dạng V-ing (chủ động) Đại từ quan hệ + tobe + V3/ed => rút động từ về dạng V3/ed (bị động) Lời giải chi tiết: 2 We talked to a young man who wanted to study in England. Đáp án: We talked to a young man wanting to study in England. (Chúng tôi đã nói chuyện với một thanh niên muốn du học ở Anh.) 3 A suspected burglar, who had been arrested by the police, has escaped. Đáp án: A suspected burglar, arrested by the police, has escaped. (Một tên trộm bị tình nghi, bị cảnh sát bắt giữ, đã trốn thoát.) 4 My uncle bought a pen that was made of gold. Đáp án: My uncle bought a pen made of gold. (Chú tôi đã mua một cây bút làm bằng vàng.) 5 She was wearing a necklace that belonged to her grandmother. Đáp án: She was wearing a necklace belonging to her grandmother. (Cô ấy đang đeo một chiếc vòng cổ thuộc về bà của cô ấy.) 6 Three men, who were coming out of the restaurant late at night, saw the robbery. Đáp án: Three men, coming out of the restaurant late at night, saw the robbery. (Ba người đàn ông mà ra khỏi nhà hàng vào đêm khuya thì nhìn thấy vụ cướp.)
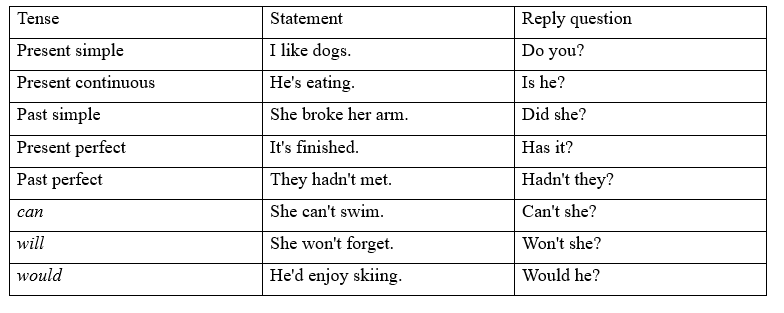
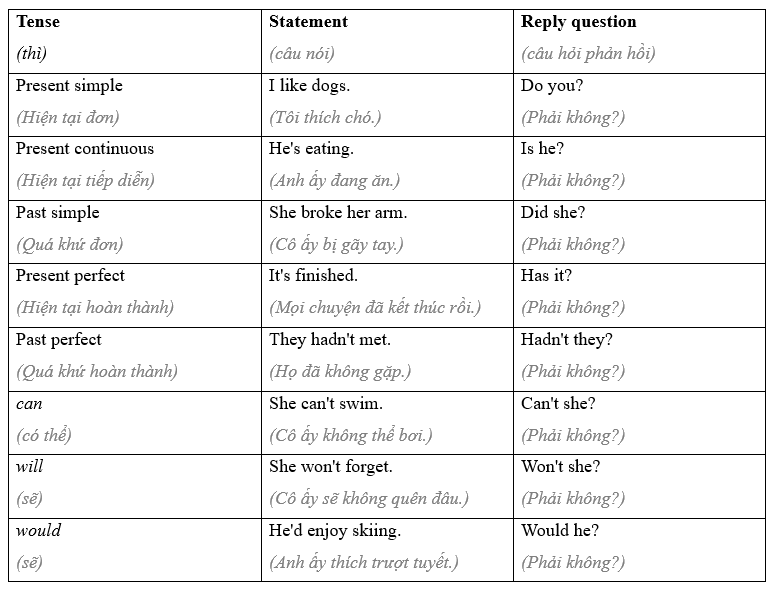
8.3 Reply questions Bài 1 8.3 Reply questions (Câu hỏi đáp trả) We use a reply question to respond to a statement. They express interest or surprise. “I've bought a new bike.” “Have you? How could you afford it?” We use the verb be, auxiliary verbs (do, have), or modal verbs (will, would, etc.), depending on the tense and verb form in the statement. 'He hasn't seen that film. 'Hasn't he? Well, let's rent it, then.' 'I hate cats' 'Do you? I thought you liked them."
Notice these special cases: I'm not hungry. "Aren't you?' NOT "You never invite me to your house." "Don't I?" "Nothing bad happened." "Didn't it?" 'Nobody wants to sit next to me.' 'Don't they?"
Tạm dịch Chúng ta sử dụng một câu hỏi đáp trả để trả lời một tuyên bố. Họ thể hiện sự quan tâm hoặc ngạc nhiên. “Tôi đã mua một chiếc xe đạp mới.” “Có thật không? Làm thế nào bạn có thể đủ khả năng đó? Chúng ta sử dụng động từ be, trợ động từ (do, have), hoặc động từ khuyết thiếu (will, would, v.v.), tùy thuộc vào thì và dạng của động từ trong câu. 'Anh ấy chưa xem bộ phim đó. 'Phải không? Vậy thì chúng ta hãy thuê nó. ' Em ghét mèo' 'Thật hả? Anh tưởng em thích chúng."
Lưu ý những trường hợp đặc biệt này: Tôi không đói. "Phải không?" (Aren’t you) KHÔNG DÙNG dạng Amn’t you?X "Anh không bao giờ mời tôi đến nhà anh." "phải không?" "Không có gì xấu xảy ra." "Phải không?" 'Không ai muốn ngồi cạnh tôi.' “Phải không?”
1 Match the reply questions (a-e) with the statements (1-5). (Ghép các câu hỏi phản hồi (a-e) với các câu (1-5).)
Phương pháp giải: Cách tạo câu hỏi phản hồi: tobe / trợ động từ / động từ khiếm khuyết + S? Lời giải chi tiết:
1 – c: Yesterday was Monday. - Was it? (Hôm qua là thứ Hai. – Phải không?) 2 – a: Nothing exciting happened on holiday. - Didn't it? (Không có gì thú vị xảy ra trong kỳ nghỉ. – Phải không?) 3 – e: Our dog had never run away before. - Hadn't it? (Con chó của chúng tôi chưa bao giờ bỏ chạy trước đây. - Phải không?) 4 – b: The train had to stop suddenly. - Did it? (Tàu phải dừng đột ngột. – Phải không?) 5 – d: My laptop has broken again. - Has it? (Máy tính xách tay của tôi lại bị hỏng. – Phải không?) 8.3 Reply questions Bài 2 2 Write reply questions for these statements. (Viết câu hỏi phản hồi cho những câu nói này.) 1 I want to go somewhere different for my holiday this year. 2 Nobody told me about your accident. 3 I'm not ready to go out yet. 4 Our friends hardly ever go out during the week. 5 It costs a lot to send texts abroad. 6 Gorillas can't swim. 7 I'd rather spend this weekend at home. 8 My parents wouldn't enjoy skiing. Phương pháp giải: Cách tạo câu hỏi phản hồi: tobe / trợ động từ / động từ khiếm khuyết + S? Lời giải chi tiết:
1 I want to go somewhere different for my holiday this year. - Do you? (Tôi muốn đi đâu đó khác biệt cho kỳ nghỉ của tôi năm nay. – Phải không?) 2 Nobody told me about your accident. - Didn’t they? (Không ai nói với tôi về tai nạn của bạn. – Phải không?) 3 I'm not ready to go out yet. - Aren’t you? (Tôi vẫn chưa sẵn sàng ra ngoài. – Phải không?) 4 Our friends hardly ever go out during the week. - Don’t they? (Những người bạn của chúng tôi hầu như không bao giờ đi chơi trong tuần. – Phải không?) 5 It costs a lot to send texts abroad. - Does it? (Nó tốn rất nhiều tiền để gửi tin nhắn ra nước ngoài. – Phải không?) 6 Gorillas can't swim. - Can’t they? (Khỉ đột không thể bơi. – Phải không?) 7 I'd rather spend this weekend at home. - Would you? (Tôi muốn dành cuối tuần này ở nhà hơn. – Phải không?) 8 My parents wouldn't enjoy skiing. - Wouldn’t they? (Bố mẹ tôi không thích trượt tuyết. – Phải không?) 8.4 Question tags Bài 1 8.4 Question tags (Câu hỏi đuôi) We use question tags when we want somebody to confirm something that we are saying. A statement with a question tag often sounds more polite than a direct question or a plain statement. You live in Madrid, don't you? When the main verb is affirmative, the question tag is negative, and vice versa. She was late, wasn't she? She wasn't late, was she? We use the verb be, auxiliary verbs (do, have), or modal verbs (will, would, etc.), depending on the tense of the verb in the statement.
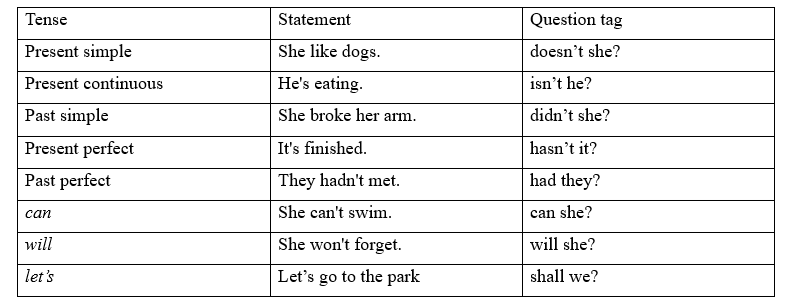
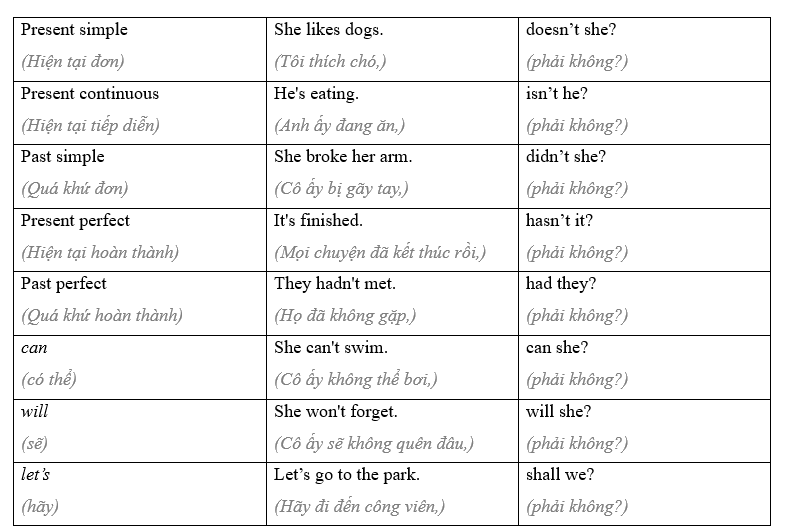
Notice these special cases: I'm the winner, aren't I? It hardly ever rains here, does it? Let's go to the park, shall we? Nothing's wrong, is it? Nobody minds if I eat the last piece, do they? Tạm dịch Chúng ta sử dụng câu hỏi đuôi khi muốn ai đó xác nhận điều gì đó mà chúng ta đang nói. Một câu nói với một câu hỏi đuôi thường nghe lịch sự hơn một câu hỏi trực tiếp hoặc một câu nói đơn giản. Bạn sống ở Madrid, phải không? Khi động từ chính ở thể khẳng định thì câu hỏi đuôi ở thể phủ định và ngược lại. Cô đến muộn phải không? Cô ấy không đến trễ, phải không? Chúng ta sử dụng động từ be, trợ động từ (do, have), hoặc động từ khuyết thiếu (will, would, v.v.), tùy thuộc vào thì của động từ trong câu.
Lưu ý những trường hợp đặc biệt này: Tôi là người chiến thắng, phải không? Ở đây hầu như không bao giờ mưa, phải không? Chúng ta hãy đi đến công viên, nhỉ? Không có gì sai, phải không? Không ai phiền nếu tôi ăn miếng cuối cùng, phải không? 1 Match the question tags below with statements 1-8. (Ghép các câu hỏi đuôi dưới đây với các câu 1-8.)
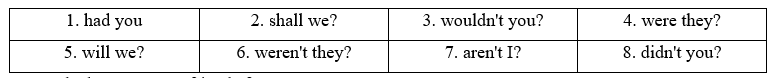
1 You hadn't seen your friends for years, __________ 2 Let's go away for a few days, __________ 3 You'd rather be alone this evening, __________ 4 Nobody was surprised at his decision, __________ 5 We won't arrive on time, __________ 6 Your parents were teachers, __________ 7 I'm the best chess player in the school, __________ 8 You had double maths this morning, __________ Phương pháp giải: Cách tạo câu hỏi phản hồi: Phủ định của tobe / trợ động từ / động từ khiếm khuyết + S? Lời giải chi tiết:
1 You hadn't seen your friends for years, had you? (Bạn đã không gặp bạn bè của mình trong nhiều năm rồi phải không?) 2 Let's go away for a few days, shall we? (Chúng ta hãy đi xa vài ngày, nhé?) 3 You'd rather be alone this evening, wouldn't you? (Bạn thà ở một mình tối nay, phải không?) 4 Nobody was surprised at his decision, were they? (Không ai ngạc nhiên với quyết định của anh ấy, phải không?) 5 We won't arrive on time, will we? (Chúng ta sẽ không đến đúng giờ, phải không?) 6 Your parents were teachers, weren't they? (Bố mẹ bạn đã là giáo viên, phải không?) 7 I'm the best chess player in the school, aren't I? (Tôi là người chơi cờ giỏi nhất trong trường, phải không?) 8 You had double maths this morning, didn't you? (Bạn có hai tiết toán sáng nay, phải không?)
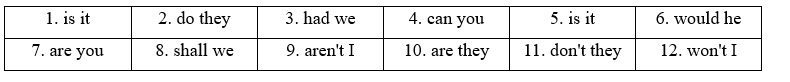
8.4 Question tags Bài 2 2 Add a question tag to these statements. (Thêm câu hỏi đuôi cho những câu nói này.) 1 It isn't too late to change my mind, __________? 2 Nobody wants to go home, __________? 3 We hadn't finished that pizza, __________? 4 You can't see my phone, __________? 5 That shop is never open, __________? 6 Your dad wouldn't give us a lift, __________? 7 You're hardly ever at home, __________? 8 Let's buy some popcorn, __________? 9 I'm your best friend, __________? 10 They aren't listening, __________? 11 Calls from abroad cost a lot, __________? 12 I'll see you soon, __________? Phương pháp giải: Cách tạo câu hỏi phản hồi: Phủ định của tobe / trợ động từ / động từ khiếm khuyết + S? Lời giải chi tiết:
1 It isn't too late to change my mind, is it? (Không quá muộn để thay đổi quyết định phải không?) 2 Nobody wants to go home, do they? (Không ai muốn về nhà phải không?) 3 We hadn't finished that pizza, had we? (Chúng ta vẫn chưa ăn xong chiếc bánh pizza đó phải không?) 4 You can't see my phone, can you? (Bạn không thể nhìn thấy điện thoại của tôi, phải không?) 5 That shop is never open, is it? (Cửa hàng đó không bao giờ mở cửa phải không?) 6 Your dad wouldn't give us a lift, would he? (Bố của bạn sẽ không cho chúng tôi quá giang, phải không?) 7 You're hardly ever at home, are you? (Bạn hiếm khi ở nhà phải không?) 8 Let's buy some popcorn, shall we? (Chúng ta hãy mua một ít bỏng ngô nhé?) 9 I'm your best friend, aren't I? (Tôi là bạn thân nhất của bạn, phải không?) 10 They aren't listening, are they? (Họ không nghe, phải không?) 11 Calls from abroad cost a lot, don't they? (Các cuộc gọi từ nước ngoài rất tốn kém phải không?) 12 I'll see you soon, won't I? (Tôi sẽ sớm gặp lại bạn, phải không?)
>> 2K9 Học trực tuyến - Định hướng luyện thi TN THPT, ĐGNL, ĐGTD ngay từ lớp 11 (Xem ngay) cùng thầy cô giáo giỏi trên Tuyensinh247.com. Bứt phá điểm 9,10 chỉ sau 3 tháng, tiếp cận sớm các kì thi.
|