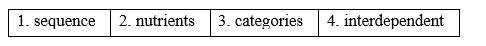Reading - Unit 10. The ecosystem - SBT Tiếng Anh 11 Global Success1. Read the text and choose the best answers. 2. Read the text and match the highlighted words with the meanings. 3. Read the text in 2 again and decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). GÓP Ý HAY - NHẬN NGAY QUÀ CHẤT Gửi góp ý cho HocTot.Nam.Name.Vn và nhận về những phần quà hấp dẫn
Lựa chọn câu để xem lời giải nhanh hơn
Bài 1 1. Read the text and choose the best answers. (Đọc văn bản và chọn câu trả lời đúng nhất.) Viet Nam’s flora and fauna With a coastline of over 3,260 kilometres, Viet Nam is (1) __________ to many different kinds of flora and fauna. From the Fansipan Peak all the way down to the Mekong Delta, the country has a rich (2) __________ of wildlife. However, due to population growth and rapid urban development, many of Viet Nam’s plant and (3) __________ species are endangered. Natural habitats are threatened by deforestation and the (4) __________ of natural resources. Several unique species have almost disappeared in recent years (5) __________ the illegal wildlife trade. The trade in animal parts continues to be a serious problem (6) __________ the heavy punishment. There is still high demand for elephant ivory, rhino horn, turtle eggs, and other wild animal parts. This has forced a number of mammals and other (7) __________ onto the Red List of Threatened Species. In 2010, Viet Nam’s last Javan rhino was shot and killed for its (8) __________. Nevertheless, there are still many other native species found in the country’s dense forests. Scientists continue to (9) __________ unique and rare animals such as the saola and the pangolin. However, if the country wants to conserve its biodiversity and fascinating features, it still has (10) __________ to go.
1. A. area B. location C. place D. home
2. A. diversity B. complex C. number D. footprint
3. A. flora B. fauna C. animal D. creature
4. A. use B. overuse C. misuse D. lack
5. A. due B. although C. because of D. because
6. A. because of B. despite C. due to D. since
7. A. things B. flora C. birds D. creatures
8. A. horn B. ivory C. eggs D. parts
9. A. list B. shoot C. meet D. discover
10. A. a lot B. a long way C. some way D. nothing Lời giải chi tiết:
1. D. home - be home to: là nhà của ai đó 2. A. diversity: sự đa dạng - rich diversity of wildlife: sự đa dạng phong phú của động vật hoang dã Các đáp án còn lại mang nghĩa không phù hợp với ngữ cảnh: B. complex: sự phức tạp C. number: số D. footprint: dấu vết 3. C. animal: động vật - plant and animal species: các loài động thực vật 4. B. overuse: việc lạm dụng, sử dụng quá mức - the overuse of natural resources: sự lạm dụng nguồn tài nguyên thiên nhiên 5. C. because of: bởi vì - cụm phía sau giải thích lý do cho mệnh đề phía trước => because of + N/V-ing Các đáp án còn lại chỉ đi với mệnh đề: A. due + to + clause B. although + clause D. because + clause 6. B. despite: mặc dù, bất chấp - Câu có hai mệnh đề mang nghĩa trái ngược => dùng “despite”. Các đáp án còn lại không phù hợp ngữ nghĩa của câu: A. because of: bởi vì C. due to: bởi vì D. since: bởi vì 7. D. creatures: sinh vật Các đáp án còn lại mang nghĩa không phù hợp: A. things: vật B. flora: hệ thực vật C. birds: chim 8. A. horn: sừng Các đáp án còn lại mang nghĩa không phù hợp: B. ivory: ngà voi C. eggs: trứng D. parts: các bộ phận 9. D. discover: khám phá Các đáp án còn lại mang nghĩa không phù hợp: A. list: lên danh sách B. shoot: bắn C. meet: gặp, đáp ứng 10. B. a long way - a long way to go: một chặng đường dài phía trước Viet Nam’s flora and fauna With a coastline of over 3,260 kilometres, Viet Nam is (1) home to many different kinds of flora and fauna. From the Fansipan Peak all the way down to the Mekong Delta, the country has a rich (2) diversity of wildlife. However, due to population growth and rapid urban development, many of Viet Nam’s plant and (3) animal species are endangered. Natural habitats are threatened by deforestation and the (4) overuse of natural resources. Several unique species have almost disappeared in recent years (5) because of the illegal wildlife trade. The trade in animal parts continues to be a serious problem (6) despite the heavy punishment. There is still high demand for elephant ivory, rhino horn, turtle eggs, and other wild animal parts. This has forced a number of mammals and other (7) creatures onto the Red List of Threatened Species. In 2010, Viet Nam’s last Javan rhino was shot and killed for its (8) horn. Nevertheless, there are still many other native species found in the country’s dense forests. Scientists continue to (9) discover unique and rare animals such as the saola and the pangolin. However, if the country wants to conserve its biodiversity and fascinating features, it still has (10) a long way to go. (Hệ động thực vật Việt Nam Với đường bờ biển dài hơn 3.260 km, Việt Nam là nơi sinh sống của nhiều loại động thực vật khác nhau. Từ đỉnh Fansipan đến tận đồng bằng sông Cửu Long, cả nước có rất nhiều động vật hoang dã đa dạng. Tuy nhiên, do sự gia tăng dân số và phát triển đô thị nhanh chóng, nhiều loài thực vật và loài động vật của Việt Nam đang bị đe dọa. Môi trường sống tự nhiên đang bị đe dọa bởi nạn phá rừng và lạm dụng tài nguyên thiên nhiên. Một số loài độc đáo gần như đã biến mất trong những năm gần đây do buôn bán động vật hoang dã bất hợp pháp. Việc buôn bán các bộ phận động vật tiếp tục là một vấn đề nghiêm trọng mặc dù bị trừng phạt nặng nề. Nhu cầu về ngà voi, sừng tê giác, trứng rùa và các bộ phận động vật hoang dã khác vẫn còn cao. Điều này đã buộc một số động vật có vú và sinh vật khác vào Danh sách đỏ các loài bị đe dọa. Vào năm 2010, con tê giác Java cuối cùng của Việt Nam đã bị bắn chết để lấy sừng. Tuy nhiên, vẫn còn nhiều loài bản địa khác được tìm thấy trong các khu rừng rậm của đất nước. Các nhà khoa học tiếp tục khám phá các loài động vật độc đáo và quý hiếm như sao la và tê tê. Tuy nhiên, nếu đất nước muốn bảo tồn đa dạng sinh học và các đặc điểm hấp dẫn của mình, nó vẫn còn một chặng đường dài phía trước.)
Bài 2 2. Read the text and match the highlighted words with the meanings. (Đọc văn bản và nối các từ được đánh dấu với nghĩa.) Food chains Each living thing can be a part of different food chains. Living things can be producers or consumers. Producers make their own food. For example, many plants are in the producers’ group as they use energy from the sun, water and nutrients from the soil. Consumers, on the other hand, don’t make their own food. Some eat producers or other consumers, such as animals, while others eat both. For example, farm animals like cows, chickens and pigs eat corn, grass, and hay because they cannot make food for themselves like many plants do. A food chain is the sequence of who eat whom in an ecosystem. For instance, the sun makes energy for the grass, which gets eaten by a zebra, which gets eaten by a lion. Or, the grass gets eaten by a cricket, which gets eaten by a snake, which gets eaten by an owl. These are all examples of food chains. Food chains show how all living things depend on each other. For example, we as consumers drink fruit juice made from a plant or producer. We also consume dairy products such as milk and cheese, which come from other consumers like cows and sheep. So producers and consumers are interdependent. There are many food chains in the various habitats on Earth. Animals that eat other animals are called predators, and the animals they eat are called prey. Consumers are divided into three categories: herbivores, omnivores and carnivores. A herbivore only eats plants, an omnivore eats plants and meat, and a carnivore only eats meat. 1. the order that actions happen in __________ 2. substances that keep a living thing alive and help it grow __________ 3. groups of people or things with particular features __________ 4. consisting of parts that depend on each other __________ Lời giải chi tiết:
1. the order that actions happen in: sequence. (thứ tự các hành động xảy ra theo: trình tự.) 2. substances that keep a living thing alive and help it grow: nutrients. (chất giữ cho một sinh vật sống và giúp nó phát triển: chất dinh dưỡng.) 3. groups of people or things with particular features: categories. (nhóm người hoặc vật có đặc điểm riêng: thể loại.) 4. consisting of parts that depend on each other: interdependent. (bao gồm các bộ phận phụ thuộc vào nhau: phụ thuộc lẫn nhau.) Tạm dịch: Chuỗi thức ăn Mỗi sinh vật sống có thể là một phần của chuỗi thức ăn khác nhau. Sinh vật sống có thể là nhà sản xuất hoặc người tiêu dùng. Các nhà sản xuất làm thức ăn của riêng họ. Ví dụ, nhiều loại cây thuộc nhóm sản xuất vì chúng sử dụng năng lượng từ mặt trời, nước và chất dinh dưỡng từ đất. Mặt khác, người tiêu dùng không tự làm thức ăn cho mình. Một số ăn thịt người sản xuất hoặc người tiêu dùng khác, chẳng hạn như động vật, trong khi những người khác ăn cả hai. Ví dụ, các động vật trang trại như bò, gà và lợn ăn ngô, cỏ và cỏ khô vì chúng không thể tự tạo ra thức ăn như nhiều loại thực vật. Chuỗi thức ăn là trình tự ai ăn ai trong một hệ sinh thái. Ví dụ, mặt trời tạo năng lượng cho cỏ, bị ngựa vằn ăn, bị sư tử ăn. Hay cỏ bị dế ăn, rắn ăn, cú ăn. Đây là tất cả các ví dụ về chuỗi thức ăn. Chuỗi thức ăn cho thấy tất cả các sinh vật sống phụ thuộc vào nhau như thế nào. Ví dụ: chúng ta với tư cách là người tiêu dùng uống nước trái cây làm từ nhà máy hoặc nhà sản xuất. Chúng ta cũng tiêu thụ các sản phẩm từ sữa như sữa và phô mai, những sản phẩm đến từ những người tiêu dùng khác như bò và cừu. Vì vậy, người sản xuất và người tiêu dùng phụ thuộc lẫn nhau. Có nhiều chuỗi thức ăn trong các môi trường sống khác nhau trên Trái đất. Động vật ăn thịt động vật khác được gọi là động vật ăn thịt và động vật ăn chúng được gọi là con mồi. Người tiêu dùng được chia thành ba loại: động vật ăn cỏ, động vật ăn tạp và động vật ăn thịt. Động vật ăn cỏ chỉ ăn thực vật, động vật ăn tạp ăn thực vật và thịt, động vật ăn thịt chỉ ăn thịt.
Bài 3 3. Read the text in 2 again and decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). (Đọc lại văn bản ở phần 2 và quyết định xem những câu sau đây là đúng (T) hay sai (F).) 1. All living things are producers. 2. Sun and soil help producers make their own food. 3. Examples of consumers are animals kept for their milk or meat. 4. Lions have become a top predator in a food chain by eating animals that feed on grass. 5. People are both consumers and producers. 6. There are very few food chains on Earth. 7. The only food that herbivores eat is meat. Lời giải chi tiết:
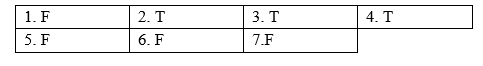
1. All living things are producers. F (Mọi sinh vật đều là nhà sản xuất.) => SAI Thông tin: “Living things can be producers or consumers.” (Sinh vật sống có thể là nhà sản xuất hoặc người tiêu dùng.) 2. Sun and soil help producers make their own food. T (Mặt trời và đất giúp người sản xuất tự kiếm thức ăn.) => ĐÚNG Thông tin: “For example, many plants are in the producers’ group as they use energy from the sun, water and nutrients from the soil.” (Ví dụ, nhiều loại cây thuộc nhóm sản xuất vì chúng sử dụng năng lượng từ mặt trời, nước và chất dinh dưỡng từ đất.) 3. Examples of consumers are animals kept for their milk or meat. T (Ví dụ về người tiêu dùng là động vật được nuôi để lấy sữa hoặc thịt.) => ĐÚNG Thông tin: “We also consume dairy products such as milk and cheese, which come from other consumers like cows and sheep.” (Chúng ta cũng tiêu thụ các sản phẩm từ sữa như sữa và phô mai, những sản phẩm mà đến từ những người tiêu dùng khác như bò và cừu.) 4. Lions have become a top predator in a food chain by eating animals that feed on grass. T (Sư tử đã trở thành kẻ săn mồi hàng đầu trong chuỗi thức ăn bằng cách ăn thịt động vật ăn cỏ.) => ĐÚNG Thông tin: “For instance, the sun makes energy for the grass, which gets eaten by a zebra, which gets eaten by a lion.” (Ví dụ, mặt trời tạo năng lượng cho cỏ, thứ bị ngựa vằn ăn, con mà bị sư tử ăn.) 5. People are both consumers and producers. F (Người dân vừa là người tiêu dùng, vừa là người sản xuất.) => SAI Thông tin: “We as consumers drink fruit juice made from a plant or producer. We also consume dairy products.” (chúng ta với tư cách là người tiêu dùng uống nước trái cây làm từ nhà máy hoặc nhà sản xuất. Chúng ta cũng tiêu thụ các sản phẩm từ sữa.) => người dân là người tiêu dùng. 6. There are very few food chains on Earth. F (Có rất ít chuỗi thức ăn trên Trái đất.) => SAI Thông tin: “There are many food chains in the various habitats on Earth.” (Có nhiều chuỗi thức ăn trong các môi trường sống khác nhau trên Trái đất.) 7. The only food that herbivores eat is meat. F (Thức ăn duy nhất mà động vật ăn cỏ ăn là thịt.) => SAI Thông tin: “A herbivore only eats plants.” (Động vật ăn cỏ chỉ ăn thực vật.)
>> 2K9 Học trực tuyến - Định hướng luyện thi TN THPT, ĐGNL, ĐGTD ngay từ lớp 11 (Xem ngay) cùng thầy cô giáo giỏi trên Tuyensinh247.com. Bứt phá điểm 9,10 chỉ sau 3 tháng, tiếp cận sớm các kì thi.
|